Table of Contents
What decibel level is safe for your ears? That’s a question that many people ask, especially if they work in a loud environment or like to listen to music loudly. It can be hard to tell what level of noise is too loud, and it’s important to protect your ears from long-term damage. In this blog post, we will discuss the decibel levels that are safe for your ears and how you can protect yourself from harmful noise.
Decibel Level Scale
The decibel (dB) is the unit used to measure sound intensity. The decibel scale is a logarithmic scale, which means that each increase of ten decibels corresponds to a ten-fold increase in sound intensity. For example, For example, a 110 decibels us tmice as loud as 100 decibels.
To give you an idea of how loud different decibel levels can be, here are some common sounds and their decibel levels:
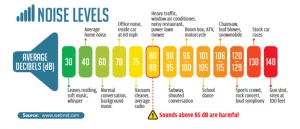
- 0 decibel – threshold of hearing
- 20 decibels – leaves rustling
- 30 decibels – quiet conversationб – Whispering
- 60 decibels – normal conversation
- 85 decibels – exposure limit for continuous noise according to OSHA
- 90 decibels – vacuum cleaner, Lawn mower
- 100 decibels – heavy traffic
- 110 decibels – rock concert or nightclub
- 120 decibels – pain threshold
- 130 decibel and up – danger level for noise exposure (can cause hearing loss)
While there are no hard and fast rules about what decibel level is safe for human exposure, it is important to take into consideration recommended guidelines to prevent hearing loss. According to OSHA, the safe decibel level is lower than 85 dB to prevent hearing damage in humans. Exposure to sounds at or above this level can lead to gradual hearing loss over time.
It is worth noting that the risk of hearing damage increases as the sound intensity and duration of exposure increase. For instance, exposure to sounds at 100 dB, such as a jackhammer, should not exceed 15 minutes per day without proper hearing protection. Sounds at 120 dB, like a rock concert, can cause immediate damage to the ears.
However, it is essential to highlight that some extremely loud sounds can be dangerous even at shorter durations. For example, a gunshot can reach around 136 dB, which is well above the safe range for prolonged exposure. Immediate and significant hearing damage can occur from exposure to such intense sound levels.
To protect your hearing, it is recommended to limit exposure to loud noises, use hearing protection devices such as earplugs or earmuffs when necessary, and maintain a safe distance from loud sources. Regular hearing check-ups are also advisable to monitor any changes in your hearing abilities and address potential issues promptly.
Safe Decibel Levels According to OSHA: Action levels and Eposure Limits
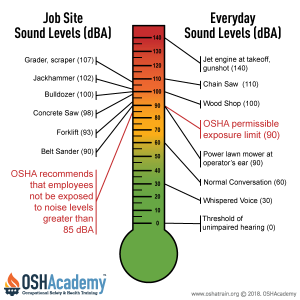
The decibel level is safe by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) (official website) when it comes to exposure in the workplace. OSHA has set a permissible exposure limit (PEL) for continuous, long-term noise exposure. For an eight hour day, the decibel level should not exceed 90 decibels. If you are exposed to noise levels above this on a regular basis, you may be at risk for hearing loss.
There are two types of PELs:
- action levels
- exposure limits.
An action level is a decibel level at which employers must provide their employees with hearing protection devices and implement a hearing conservation program. The action level for continuous, long-term noise exposure is 85 decibels.
An exposure limit is the decibel level at which employers must take action to reduce employee noise exposures. The exposure limit for continuous, long-term noise exposure is 90 decibels.
If you are worried about your exposure to loud noise at work, make sure to ask your employer about their hearing conservation program and what they are doing to reduce noise levels. You can also request a copy of the OSHA PELs from your employer. And, of course, make sure to wear hearing protection when you are exposed to loud noise!
Machinery producing Too Loud Sounds
Some of the machinery that can produce too loud sounds are:
- agricultural equipment such as tractors, combines, and hay balers;

- construction equipment such as jackhammers and bulldozers;
- awn care equipment such as leaf blowers, mowers, and trimmers;
- power tools such as drills, saws, sanders, and routers;
- factory machines such as press brakes, stamping machines, textile machinery, and woodworking machinery.
All of these machines can generate decibel levels that exceed 85 dB. When decibel levels exceed 85 dB on a regular basis, it can lead to hearing loss. If you work with any of these machines on a regular basis, it’s important to wear ear protection to prevent hearing loss.
Importance of Noise Measuring Levels at Your Workplace
In many situations, a risk assessment for noise at your workplace may be prepared without using equipment to measure noise levels. A realistic estimate of worker exposure is required. It is essential to understand safe decibel levels for humans to accurately assess the risk and take appropriate measures.
Safe decibel levels for humans refer to the threshold at which sound becomes potentially harmful to human hearing. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established guidelines for permissible exposure limits (PEL) to protect workers from excessive noise exposure. According to OSHA, the permissible exposure limit for an 8-hour workday is 90 decibels (dB).
If you want to get a snapshot of an employee’s day-to-day life at work, check out the various tools they use while on duty. You can also observe work activities and calculate exposure time over part of the day to estimate safe decibel levels and exposure during a full shift. If an employee is exposed to noise from more than one tool or work process throughout the course of a typical day, record information about each source’s expected noise level(s) and duration (if known).

Decibel levels produced by equipment may be obtained from manufacturers or suppliers only if there is cause to believe they are incorrect, such as when machinery or equipment is being used in a manner not specified by the manufacturer or supplier, or in other cases where noise exposure may be increased or modified.There are several phone apps that can be used to measure noise. They’re seldom precise, but they may give an indication of the noise emission levels.
As you can see, even relatively low decibel levels can be quite loud. And at high decibel levels, even a short exposure can be dangerous. So if you’re ever exposed to loud noise, make sure to take precautions to protect your hearing.
Tips for Reducing Noise Exposure
1. Noise-Cancelling Headphones and Earplugs
One effective way to reduce noise exposure is by using noise-cancelling headphones and earplugs. These devices work by actively reducing or blocking out external sounds, allowing you to enjoy a quieter environment. Noise-cancelling headphones use built-in microphones to analyze surrounding sounds and produce an opposing sound wave that cancels out the incoming noise. This technology is particularly useful in environments with constant background noise, such as offices, public transportation, or airplanes.
Earplugs, on the other hand, are inserted into the ear canal to physically block and absorb sound waves. They come in various types, such as foam, silicone, or custom-molded, offering different levels of noise reduction. Earplugs are convenient and portable, making them suitable for situations where you need quick and temporary noise protection, like studying in a noisy café or attending a loud event. When used correctly, both noise-cancelling headphones and earplugs can significantly reduce your exposure to harmful noise levels and provide a more peaceful auditory experience.
2. Techniques for Minimizing Noise Pollution in Daily Life
In addition to using noise-cancelling devices and creating quiet environments, there are various techniques you can incorporate into your daily life to minimize noise pollution. One effective approach is to schedule dedicated quiet times or noise-free periods during the day, where you can engage in activities that promote relaxation and focus, such as reading, meditation, or listening to calming music.
Practicing mindfulness and deep breathing exercises can also help you manage stress and reduce the impact of external noise on your well-being. When possible, choose quieter modes of transportation or routes to avoid excessive noise exposure during your daily commute. If you live in a noisy neighborhood, consider using white noise machines or fans to create a consistent background sound that masks disruptive noises. Finally, it’s important to be mindful of your own noise-generating behaviors, such as playing loud music or using power tools, and be considerate of others by minimizing unnecessary noise in shared spaces.
3. Creating a Quiet Environment at Home and in the Workplace
To minimize noise exposure in your living and working spaces, it’s important to create a quiet environment. Start by identifying the main sources of noise and implementing measures to reduce them. For example, you can add weatherstripping to doors and windows to seal out external noise, use heavy curtains or acoustic panels to absorb sound reflections, and place rugs or carpets on hard floors to dampen impact noise.
If you have control over the layout of your space, consider arranging furniture and objects strategically to create barriers that block or redirect sound waves. Additionally, investing in soundproofing materials, such as soundproofing foam or insulation, can further enhance the acoustic quality of your environment. Creating a quiet workspace or study area at home can help improve concentration and productivity, while implementing noise-reduction measures in the workplace can contribute to a healthier and more comfortable working environment.
4. Reducing Noise Produced by Equipment and Machinery
If you’re worried about exposure to loud noise, there are a few things you can do to protect your hearing.
You can try to reduce noise from machinery using engineering solutions, such as:
- lining guards/panels with noise dampening material
- providing acoustic screens
- lining the inside of hoppers with impact-deadening material
- fitting anti-vibration mountings
- fitting silencers to exhaust systems
- ensuring good maintenance to stop rattles and prevent noise from wear.

Wearing earplugs or other forms of ear protection is always a good idea when you know you’ll be exposed to loud noise. Earplugs and earmuffs are both effective at reducing noise levels. There are a variety of earplugs and earmuffs available that can help protect your hearing from loud noises. When choosing ear protection, it’s important to select a product that has been tested and approved by a reputable organization, such as the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
If you’re not sure what kind of ear protection to use, ask your employer or a professional for advice. If you can’t avoid the noise altogether, try to take breaks often and give your ears a chance to rest. Make sure to have your hearing checked regularly so that any damage can be caught early.
By implementing these tips for reducing noise exposure, you can create a more peaceful and conducive environment for studying, working, and daily activities, while also protecting your hearing health in the long run.
Conclusion
As you can see, decibel levels can be quite dangerous, even at relatively low levels. It depends on the loudness of the noise and the length of time you are exposed to it. If you are worried about exposure to loud noise, there are a few things you can do to protect your hearing. You can both soundproof the enviromental machinery and protect your ears by earplugs. And, of course, have your hearing checked regularly.
Do you have any other tips for protecting your hearing from loud noise? Share them in the comments below!